What is macro?
💡 Macro is a feature that generates code during compilation. Unlike macros in C, which work like “find and replace”, Swift macros are type-safe and context aware, making them powerful tools reducing boilerplate code.
Two types of macros
- attached - use
@prefix, tied to a declaration adding extra logic to it, like:@Test,@Model,@Observable - freestanding - use
#prefix, standalone code that can be invoked independently as a part of the code, like#expect,#Predicate,#warning
Example of attached macro ⤵️
@Test func addition() { // tied to the declaration
...
}
Example of freestanding macro ⤵️
@Test func addition() {
#require(1 + 2 == 3) // not attached to a declaration
}
Bonus
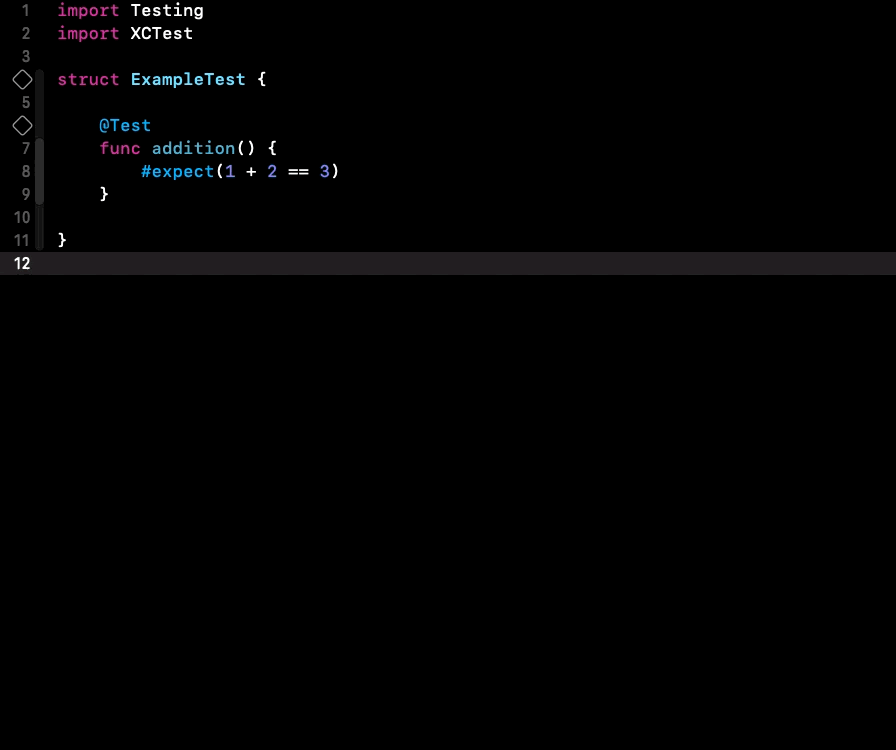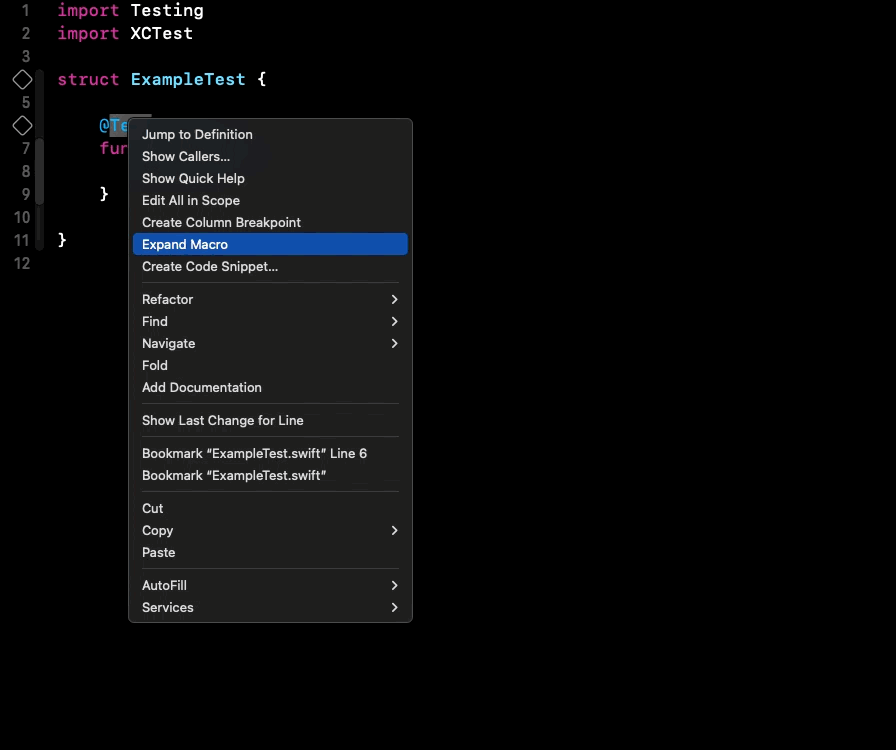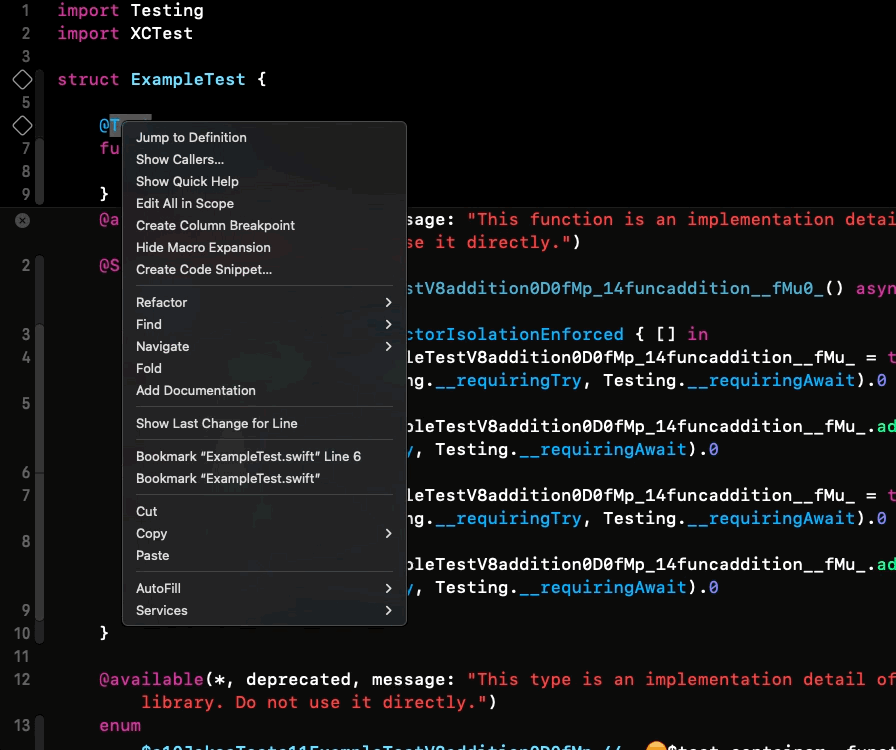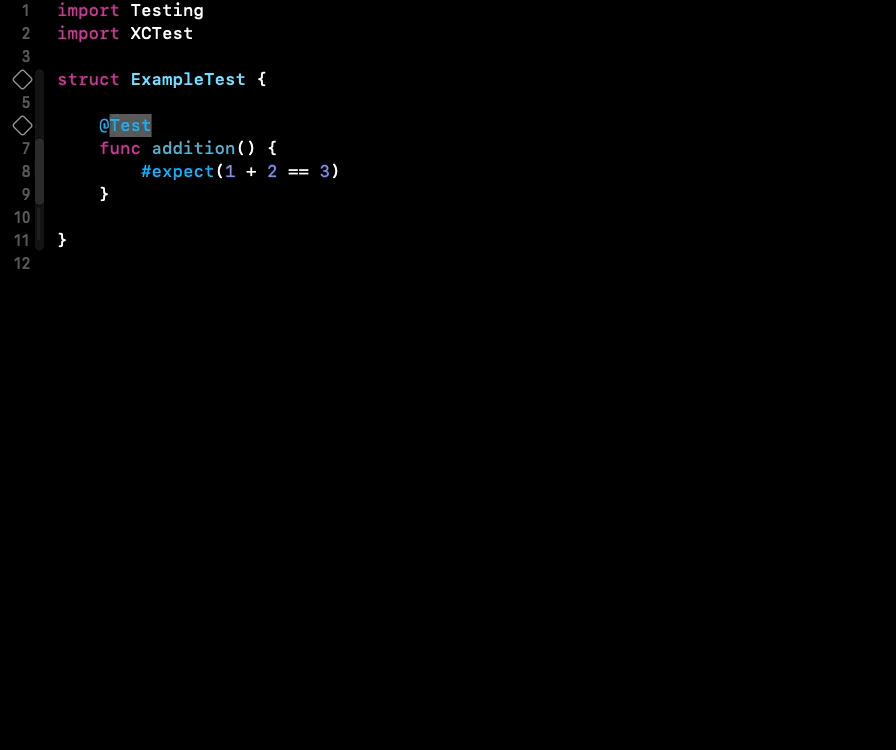
It’s possible to expand macros, especially those defined by you, and check their implementation by right-clicking on a macro and selecting the “Expand Macro” option. ⤵️
Resources
Thanks for reading. 📖
I hope you found it useful!
If you enjoy the topic don’t forget to follow me on one of my social media - LinkedIn, X, Mastodon, Bluesky or via RSS feed to keep up to speed. 🚀
